Expanding Your Kitchenware Brand: Evaluating Different Sales Channels
In May, Lifetime Brands, Inc. unveiled its 2023 Investor Report, offering valuable insights into the company’s revenue streams. For a detailed look at the report, you can view it directly here.
Overview of 2023 Lifetime Brands Investor Report
Lifetime Brands Inc. is a globally recognized leader in designing, developing, and marketing a wide array of branded consumer products for home use. The group’s proprietary brands cater to two distinct consumer segments:
- Home Users: These consumers purchase household appliances, groceries, and daily cooking and dining products through various sales channels to enrich their family life.
- Professional Chefs & Commercial Sector: These segments source professional-grade kitchenware, baking tools, and kitchen appliances from distributors to enhance operational efficiency and standardize cooking processes.

The Investor Report outlines Lifetime Brands’ performance, detailing the types of sales channels utilized, their respective proportions, and the overall scale of their effectiveness within the mature brand trading group. As stakeholders in the kitchenware industry, we can derive valuable insights from these channels to foster our business growth.
Lifetime Brands’ Key Sales Channels
The Investor Report categorizes Lifetime Brands’ terminal channels as follows:

Exploring the Pros and Cons of Various Sales Channels
When assessing different sales channels for your kitchenware brand, understanding the advantages and drawbacks is crucial for strategic decision-making.
1. Mass Market
Mass Market refers to a segment of the consumer market where products are produced in large quantities and are aimed at a broad audience. These products are typically designed to meet the everyday needs and preferences of a wide range of consumers. They are sold through widely accessible distribution channels such as supermarkets, department stores, and online platforms, such as Walmart, Target, and Fred Meyer.


2. Supermarkets
Supermarkets typically refer to large retail stores primarily focused on meeting consumers’ daily life needs, like meijer, Kroger, Publix, Safeway, BI-LO Grocery, etc. They sell a variety of goods including food, household items, and clothing. Supermarkets feature extensive floor space, offer a wide selection of products, and operate on a self-service shopping model.

3. Off-Price
The Off-Price channel refers to retail outlets that sell goods at discounted prices. This typically includes discount stores, outlet malls, and factory outlet stores, such as T.J.MAXX, ROSS, BIGLOTS!, and Burlington, providing consumers with the opportunity to purchase brand-name products at lower prices.

4. Warehouse Clubs
Warehouse clubs often carry a wide range of items from groceries and household goods to electronics and clothing, appealing to both individual consumers and businesses looking to buy in bulk. Some warehouse clubs like Costco, Sam’s Club, and BJ’s Wholesale are essentially large-scale retail stores where customers can purchase goods in bulk at discounted prices.


5. Department Stores
Department stores like Macy’s, Bloomingdale’s, Dillard’s, Kohl’s, and Belk are retail establishments that offer a wide range of products across various departments under one roof. They typically cater to diverse consumer needs, providing everything from clothing and accessories to home furnishings, cosmetics, and electronics. These stores are known for their spacious layouts and organized departmental divisions, making shopping convenient and comprehensive for customers seeking a variety of items in a single visit. Additionally, department stores often feature prominent brands and designer collections, aiming to appeal to a broad spectrum of shoppers with different tastes and preferences.

6. Specialty Stores
Specialty stores are retail outlets that specialize in specific product categories or niche markets. Unlike department stores that offer a wide range of products, specialty stores focus on a particular area such as gourmet foods, kitchenware, home decor, or outdoor gear. These stores typically curate their inventory to cater to enthusiasts and aficionados who appreciate high-quality, unique, or hard-to-find items.
Specialty stores like Williams Sonoma, Crate & Barrel, and Sur La Table are retail establishments that often provide a specialized shopping experience with expert knowledge and personalized service, aiming to attract customers seeking unique or premium products that may not be widely available in traditional retail outlets. They aim to create a distinctive atmosphere and showcase products that emphasize craftsmanship, innovation, and sometimes exclusivity, appealing to consumers seeking specialized products and a deeper level of engagement with their purchases.

7. Commercial
A commercial setting refers to business-to-business (B2B) channels where goods and services are exchanged between companies rather than directly with consumers. This includes entities like Restaurant Depot, US FOODS, and DON, which cater specifically to businesses in the food service industry. These establishments provide wholesale products and services tailored to the needs of restaurants, hotels, and other food-related businesses. They play a crucial role in supplying bulk quantities of food, beverages, and kitchen supplies, often at competitive prices designed to meet the demands of commercial operations. This channel focuses on efficiency, reliability, and meeting the specific requirements of professional customers in the food industry.

8. E-commerce/TV
E-commerce and TV shopping channels refer to retail channels where products are sold online or through televised broadcasts, appealing directly to consumers. Both of them capitalize on technology and consumer engagement strategies to enhance the shopping experience, whether through digital interfaces or live broadcasts, catering to diverse consumer preferences and shopping behaviors.
Companies like Amazon and Wayfair dominate the e-commerce space, offering a wide range of products accessible via digital platforms. These platforms provide convenience, extensive product selections, and often competitive pricing, catering to a broad audience seeking ease of shopping from home. On the other hand, QVC and HSN (Home Shopping Network) specialize in TV shopping, leveraging televised broadcasts to showcase and sell products. They engage viewers through live demonstrations and interactive presentations, emphasizing product features and benefits to encourage immediate purchases. These channels blend entertainment with shopping, fostering a direct connection between brands and consumers through engaging storytelling and persuasive demonstrations.

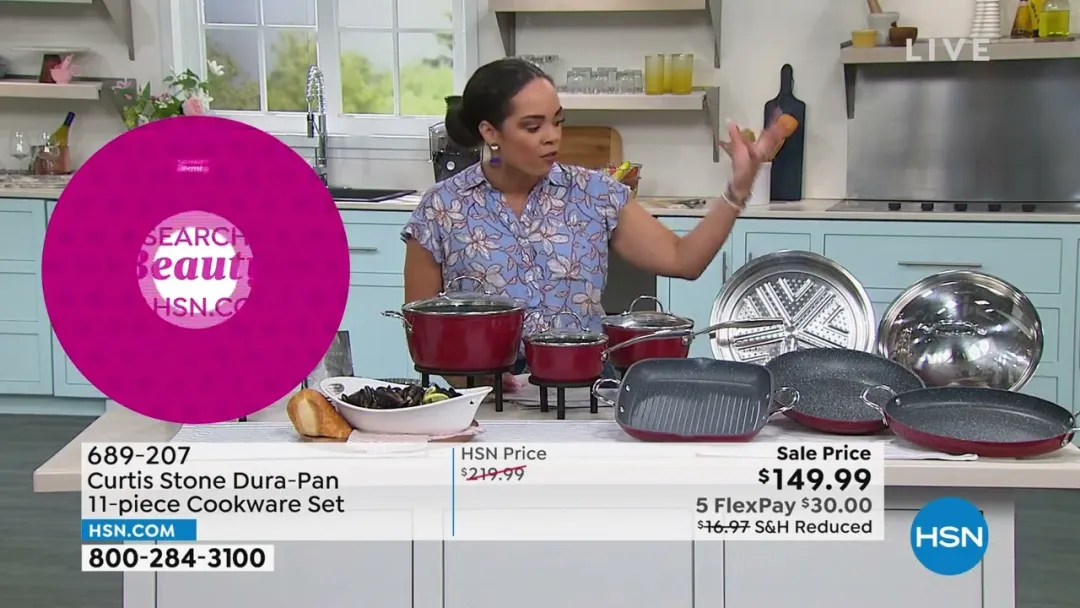
9. Independent Retailers
Independent retailers, including small local stores, are businesses that operate independently and are typically owned and managed by individuals or small groups rather than being part of a larger corporate chain. While independent retailers face challenges such as competition from larger chains and online retailers, they often distinguish themselves through their personalized service, unique product offerings, and commitment to supporting local economies.


10. Direct-to-Consumer (DTC)
Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) is a business model where brands sell products directly to consumers, bypassing traditional retail intermediaries, distributors, or wholesalers. Companies under this model manage their own sales channels, including online platforms like e-commerce websites, physical brand stores, pop-up shops, and dealer events (such as brand websites and offline showrooms). DTC empowers brands with full control over pricing, marketing strategies, and customer relationships. This direct approach allows brands to offer products directly to consumers, potentially yielding higher profit margins compared to selling through third-party retailers.


Choosing the Right Sales Channel for Your Kitchenware Brand
Choosing the optimal sales channel for your kitchenware brand is crucial for achieving sustained growth and market penetration. Each channel presents distinct advantages and challenges, tailored to different consumer segments and business strategies. Selecting the right distribution channel hinges on a deep understanding of your brand’s market positioning, target audience, and strategic objectives. Careful consideration of these factors will pave the way for successful expansion in the competitive kitchenware industry.
At SHUANGYI, we understand the importance of choosing the right distribution channels to showcase premium stainless steel kitchenware products. Whether you’re a home chef seeking quality tools or a commercial entity optimizing kitchen efficiency, our diverse range meets your needs. Explore our catalog and connect with us today!







